Ground Penetrating Radar
(GPR or Georadar)
Ground Penetrating Radar
(GPR or Georadar)


We use GPR for:
• Highways & Road Pavement Investigations
• Runways & Airport Pavements Investigations
• Locating lost/buried structures
• Service and Utility mapping
• Construction information
• Construction variation
• Rebar location mapping
• Pile cap location
• Rebar depth of cover
• Abutment backfill investigations
• Bridge deck surfacing & Material quantity evaluations
• Concrete defects
• Chimney flue mapping
• Delamination mapping
• Void mapping
• Relative moisture mapping
• Archaeological Prospecting
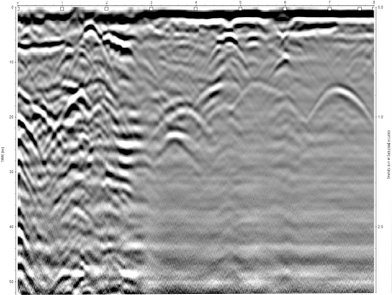

Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR) methods rely on observing the reflections from short duration pulses of electromagnetic energy. These pulses or scans are transmitted into the subject under investigation and reflections from material boundaries or embedded features (rebar’s, services or voids) are detected by a receiver.
The time duration between each scan and reflected signal is recorded in conjunction with a distance between scans to provide a continuous cross section of the subject under investigation enabling rapid assessment of thickness and condition over large areas. By assessing specific elements of the received signals it is possible to determine material thickness and construction changes. In many cases it is often possible to assess cracking and changes in compaction, bond and relative moisture content.
It should be noted that Ground Penetrating Radar does have its limitations. Understanding these limitations is the key to getting the best results from the technique.
River Crane (UK)
Edinburgh (UK)
RAF Leuchars (UK)

Utsi Electronics Ground Vue 3 GPR system
Please do not copy/use our images
without our express permission.
Thanks.